Governance
At ZERYARegenerativa, our mission is to contribute to the regeneration of agricultural and food systems, with a holistic and sustainable approach. We therefore use the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the European Union’s 2030 Agenda to guide our actions and evaluate our results. We had the privilege of participating in ONEPLANET case study with the United Nations..
With transparency
We use a rigorous and transparent methodology to measure the positive social, environmental and economic impact of our program. Thus, we can identify areas for improvement and good practices that favor regeneration. A paradigm shift reflected in our joint work on the UN road-testing report..
Our vision is long-term and takes into account the effects of our interventions on the ecosystem and future generations. We want to leave a positive and lasting legacy on the planet and people.
To this end, we offer tools and support to producers who participate in our program, so that they can continuously improve their management and profitability, while protecting the environment and the health of consumers.
Based on measurable data
Our vision is to regenerate not only the crops, but also the future of the next generations, taking care of the environment, health and well-being of people and communities.
To this end, we measure the positive impact that the implementation of our program has on each of the links in the agri-food chain, from the field to the table. In this way, we contribute to making the SDGs a reality, especially SDG 3 (Health and Well-being), SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure) and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
In addition, we create alliances among all the actors involved in the agri-food sector, fostering collaboration, transparency and trust. In this way, we respond to the demands of consumers, who are increasingly looking for responsible retailers and committed to sustainable development.
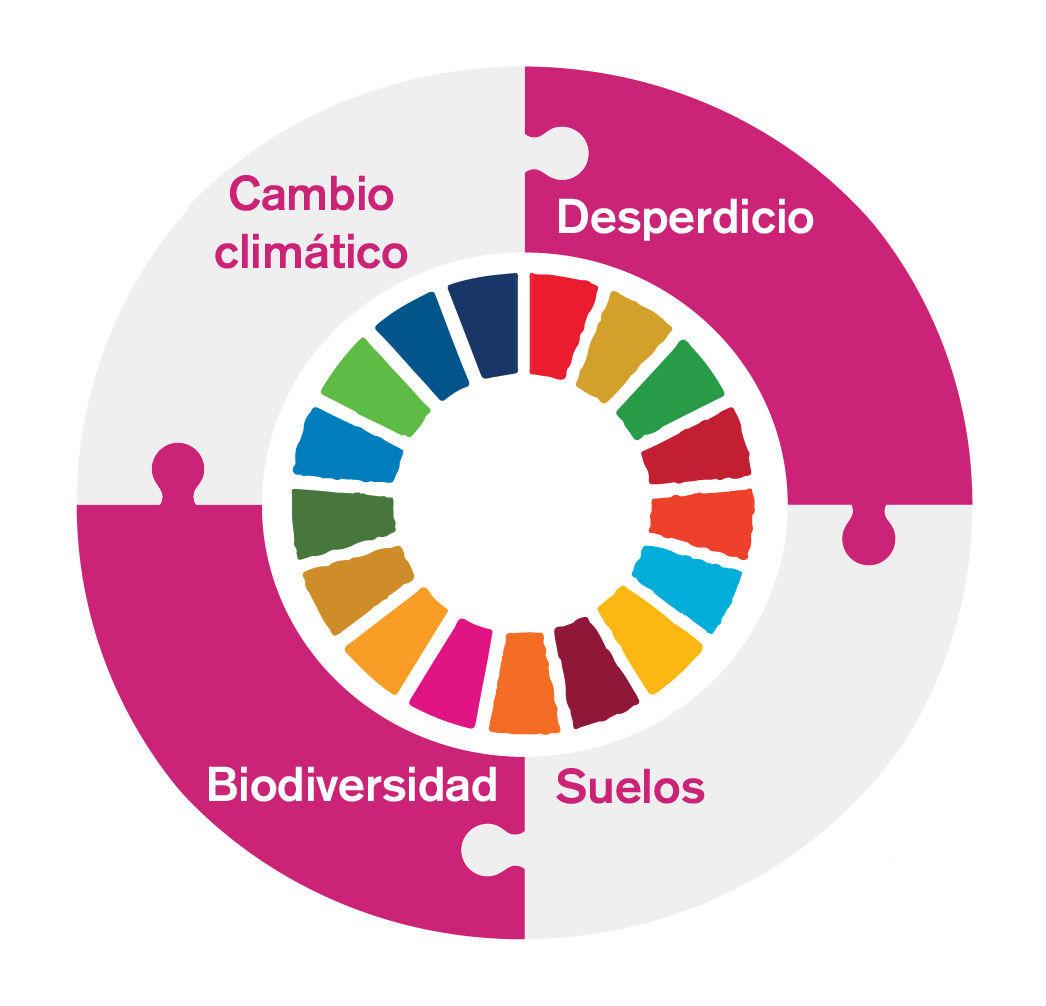
Continuous improvement with real impact
Soil erosion
Use of vegetative covers.
Use of organic matter
Optimization of fertilizer use
Water control measures
Soil microbiome analysis
Climate change
Carbon footprint calculation
Identification of improvement of the activities with the highest CO2 emissions.
Use of fossil and renewable energies
Efficient water consumption
Biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation
Agro-ecological measures such as integrated pest management (IPM).
Decrease in the use of phytosanitary inputs
Respecting watercourses and contour lines
Food waste
Agronomic yield management.
Production surpluses
Regenerative agriculture focuses on soil health and biodiversity. Some of the crops recommended for regenerative agriculture are fruit and citrus trees. Additionally, crop rotation is a common practice in regenerative agriculture and can help improve soil health.
Organic farming and regenerative farming share some principles and practices, but regenerative farming focuses on creating sustainable and regenerative agricultural systems that promote biodiversity and restoring healthy ecosystems, while organic farming focuses on the production of foods without the use of synthetic chemicals. Although organic farming refers to a broader term, which includes different types of agriculture that, such as regenerative agriculture, minimize the impact of agricultural activity on the land.
SDG 2030 Trends
Download the SDG trend sheet








